Quickstart
Let's write our first crul query!
Writing a query
Let's start with a simple use cases. We want to use the GitHub API to determine which members of our organization have expired keys that are still public.
Example
Expired GitHub GPG Keys
The query in this quickstart will list all public members in Netflix's GitHub organization, retrieve each users GPG keys, then compare their expiration time to the current time, and return a list of user emails with expired keys.
Stage 1
We will start with a single API request in our first stage, as simple as it gets!
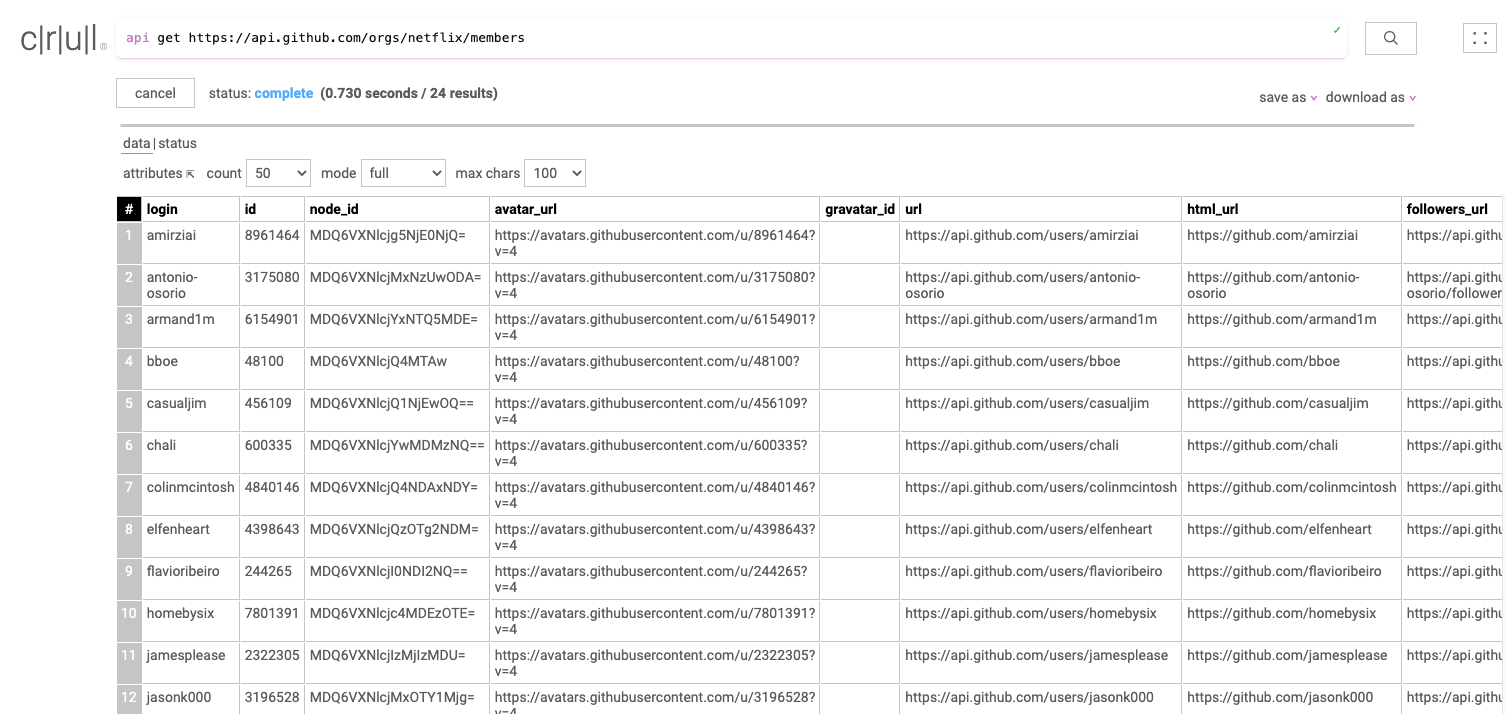
api get https://api.github.com/orgs/netflix/members
Running the query above will make an HTTP GET request and return the response in a table. The response is a table containing all the public members of Netflix's GitHub organization.
Check out some of the available flags for the api command. Flags allow for finer grained control of our stage! For the api you can use flags to set custom headers, pass in credentials, and much more!
Stage 2
For our next stage, we will take the result of our first request, and make an API request to a different endpoint for each row in order to retrieve that particular user's GPG keys.
Notice the --enrich flag, which tells the stage to enrich the previous row with the response.
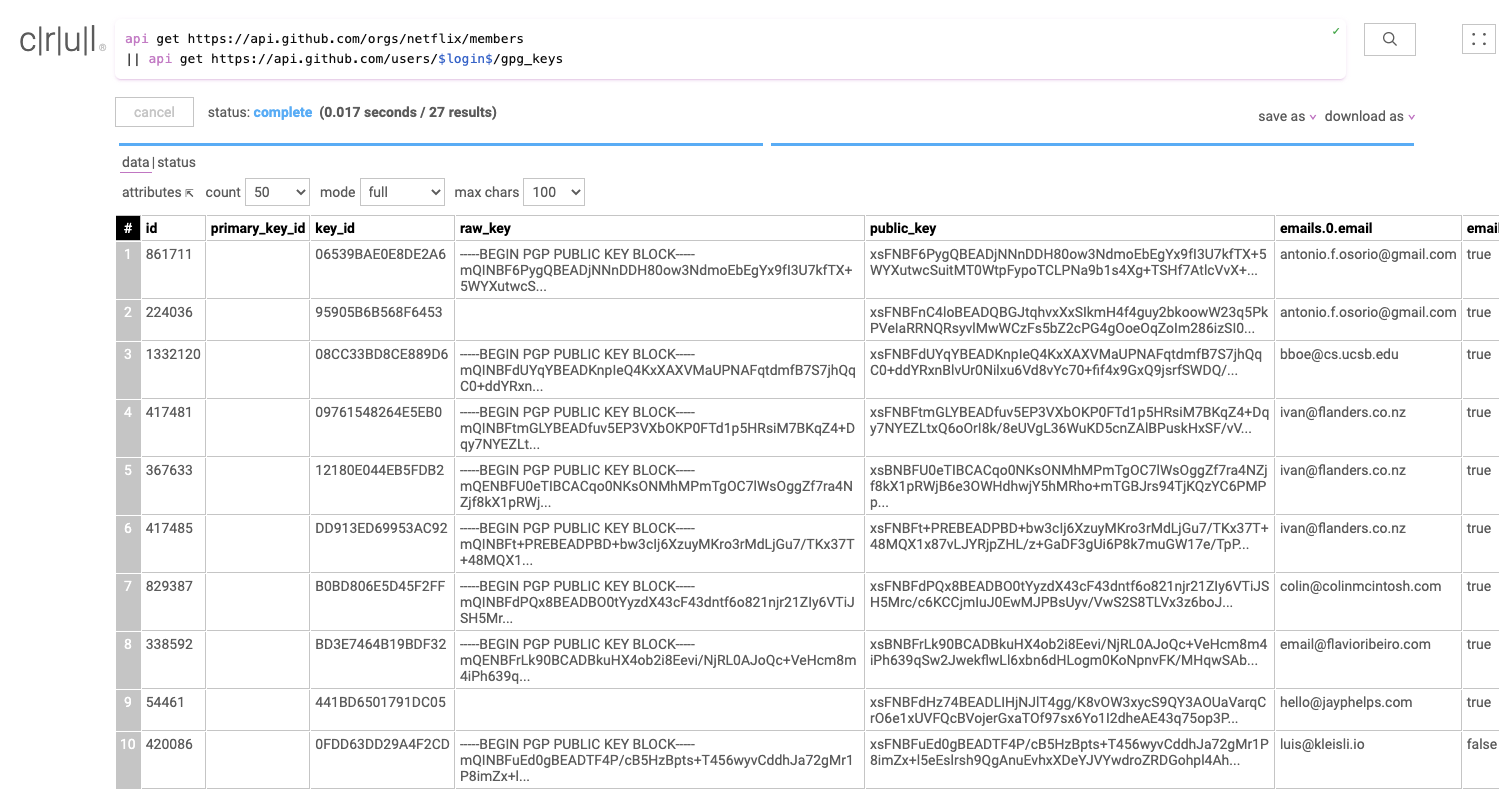
api get https://api.github.com/orgs/netflix/members
|| api get https://api.github.com/users/$login$/gpg_keys --enrich
After running this query we have a table containing all the GPG keys, as well as the user information from our first API request.
Stage 3
For our third stage, we will use the timestamp command to add the current time to our data set. We just transformed these api responses into time series data.
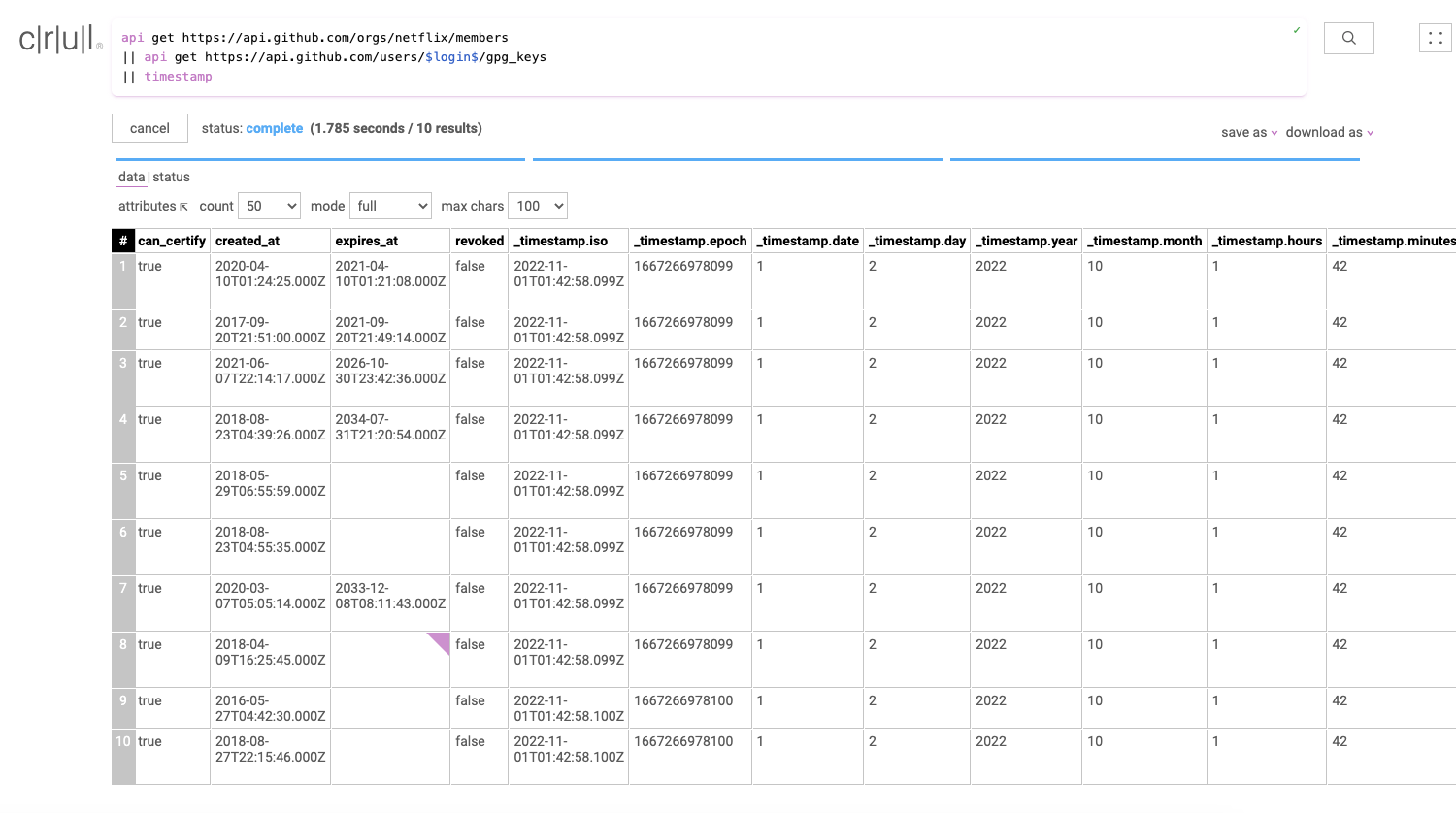
api get https://api.github.com/orgs/netflix/members
|| api get https://api.github.com/users/$login$/gpg_keys
|| timestamp
Our data set now has several new timestamp fields named _timestamp.iso, _timestamp.epoch, _timestamp.month, etc.
Stage 4
Let's run a logical operation on this data. After all, we're only interested in expired keys! We can use the filter command to filter any keys whose expires_at field is older than the current time (_timestamp.iso) that we just added in the previous stage.
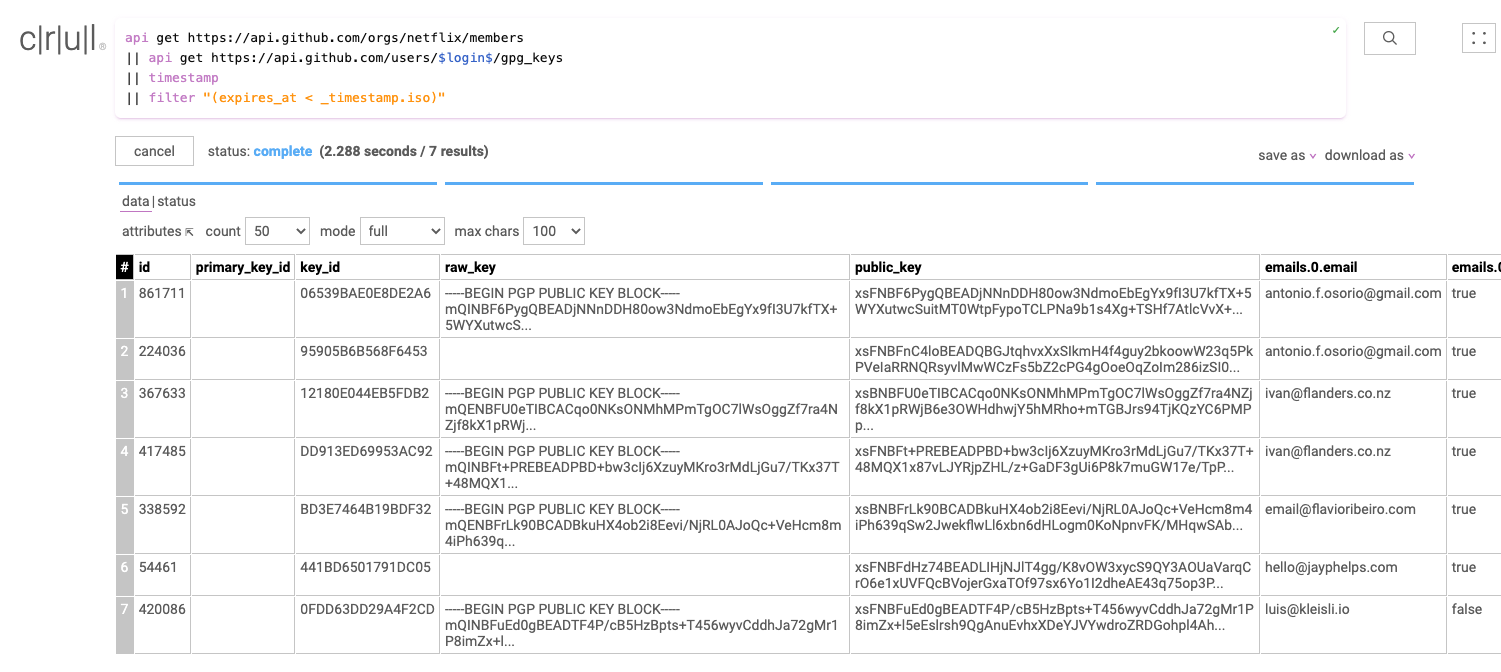
api get https://api.github.com/orgs/netflix/members
|| api get https://api.github.com/users/$login$/gpg_keys
|| timestamp
|| filter "expires_at < _timestamp.iso"
Our data set now only contains keys that have expired, or have no expiration date.
Extra credit! You can remove keys with no expiration date from the results by changing our filter to "expires_at < _timestamp.iso and expires_at != null"
Stage 5
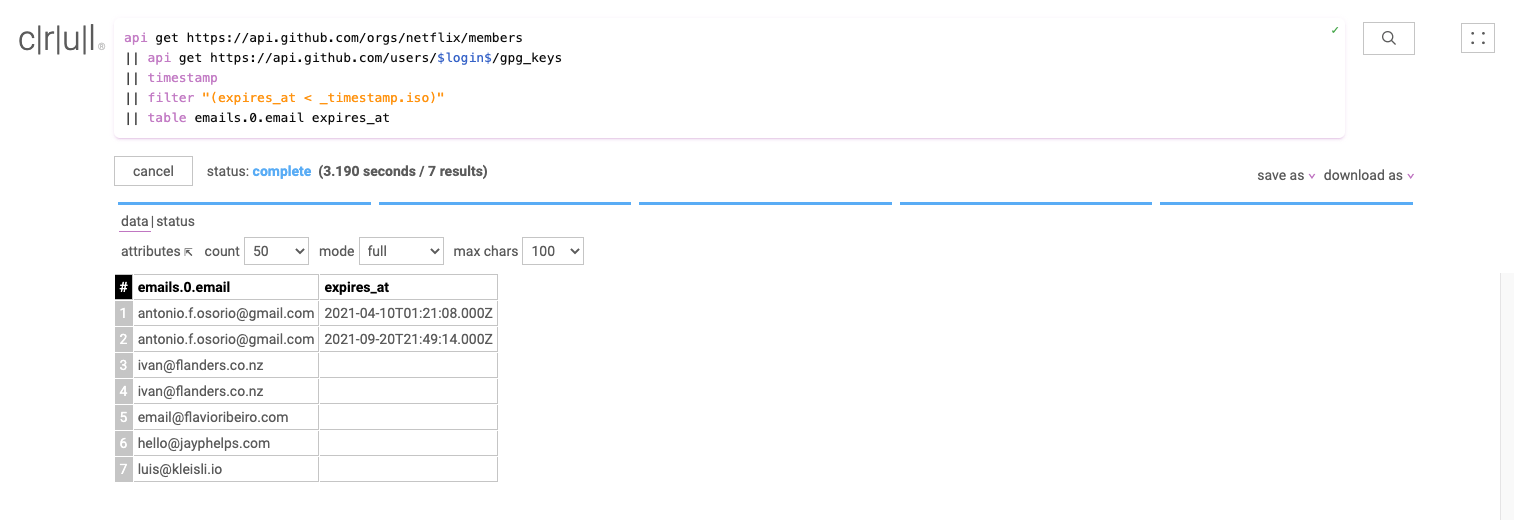
Our last stage is really simple. We'll use the table command to keep only two of the columns and remove the rest.
api get https://api.github.com/orgs/netflix/members
|| api get https://api.github.com/users/$login$/gpg_keys
|| timestamp
|| filter "expires_at < _timestamp.iso"
|| table emails.0.email expires_at
When this query was written, 7 members had expired keys, this may no longer be the case!
Nice one!
You have run your first crul query! Pretty cool no? This only scratches the surface of the capabilities of crul. If you would like a local copy of your query results, click on download as to save this as a csv or json file. To learn more about crul, check out the introduction next.
Have fun and join us on slack!